Functional Magnet-Resonance-Imaging (fMRI)
The search for the anatomic basis of psychological processes increasingly determines the focus of cognitive and emotion research. The application of functional magnet resonance imaging (fMRI) opens a non-invasive access to the study of the involved brain structures with high spatial resolution by measuring local metabolic brain activity.
Technology
Functional magnetic resonance imaging is a relatively new technique. With fMRI, the consumption of oxygen needed for metabolic processes is made visible. Here the different magnetic properties of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin in the blood are used. Activation of cortical areas leads to an increase in metabolism, the available oxygen is consumed. The more deoxygenated hemoglobin is present, the stronger the magnetic field of the hemoglobin interferes with that of the MRT.
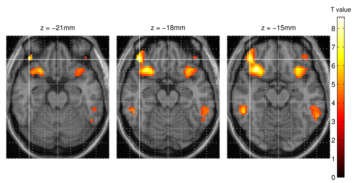
This effect is called blood oxygen level dependency (BOLD) effect. In the activated areas, it comes to a disproportionate increase in blood flow. This leads to an increase in the concentration of oxygenated hemoglobin relative to deoxygenated hemoglobin which in turn leads to an improved signal. Differences between rest and stimulation can be compared statistically with each other and the differences in activity can be assigned to the respective brain regions.
The BOLD effect though does not directly reflect neural activity. It describes the hemodynamic response, which probably is provoked by the ongoing neural activity. Therefore, neuronal activity is measured indirectly. With fMRI cortical responses to external stimuli can be measured with high spatial resolution. However, the temporal resolution e.g. compared to the EEG is low, since the BOLD response is a slow signal (4-6 seconds).
Lab
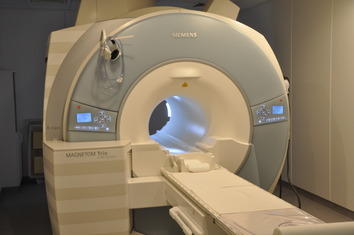
The functional imaging lab of the D.I.N.E. houses a Siemens Tim Trio (3T) magnet resonance tomograph, including 12 - and 32 - channel head coils to measure the hemodynamic response. Two eye tracking systems are available for simultaneous recording of the eye gaze in emotion situations.